
The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer. It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago. It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with beads mounted on them. The beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations. Abacus is still used in some countries like China, Russia and Japan.
A computer is a programmable electronic device that accepts raw data as input and processes it with a set of instructions (a program) to produce the result as output. It renders output just after performing mathematical and logical operations and can save the output for future use. It can process numerical as well as non-numerical calculations. The term "computer" is derived from the Latin word "computare" which means to calculate.
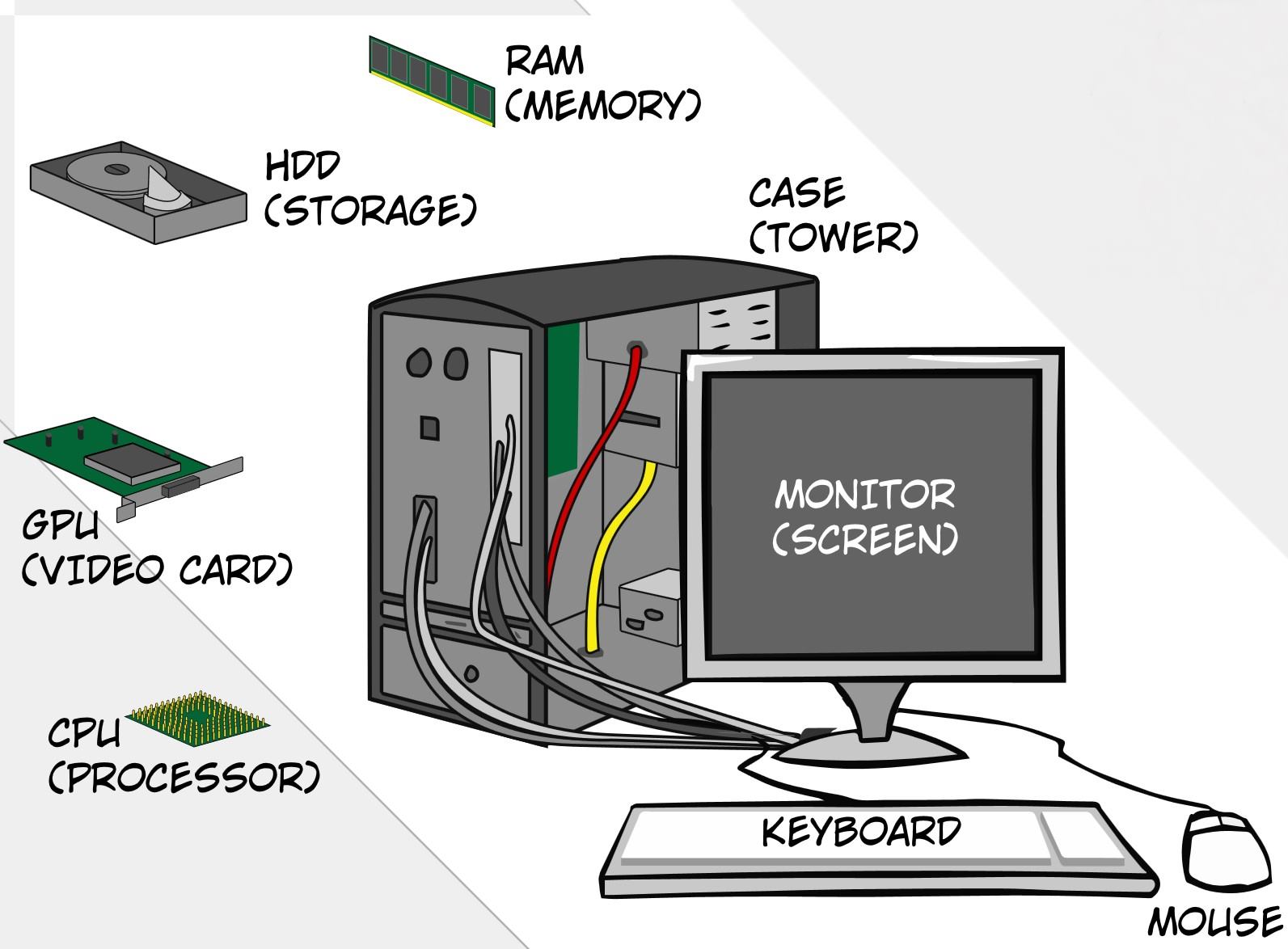
There are many components involved in building a computer. Some of the main components are:
Input devicies: Devices that accept raw data, instructions and information into the computer. It is performed with the help of input devices.
CPU: It converts the raw data into useful information. It takes the raw data from storage, processes it and then sends back the processed data to storage.
Motherboard:
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals.
Output Devices: It presents the processed data through output devices like monitor, printer and speakers.
Memory: The computer has primary memory and secondary storage to store data and instructions. It stores the data before sending it to CPU for processing and also stores the processed data before displaying it as output.